前言
在之前的文章中,讲解了使用redis解决集群环境session共享的问题【快学springboot】11.整合redis实现session共享,这里已经引入了redis相关的依赖,并且通过springboot的配置,实现了session共享。下面,我们就通过springboot提供的RedisTemplate来操作redis。
注入RedisTemplate
1
2
| @Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
|
这里我注入了一个StringRedisTemplate,其等价于RedisTemplate<String,String>,我们也可以自定义一个RedisTemplate,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @Configuration
public class RedisTemplateConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
return template;
}
}
|
本人觉得,完全没有必要自定义一个RedisTemplate,除非说有一些序列化上的需求。本文的讲解都是基于默认的StringRedisTemplate的。
设置/获取值
我们可以通过opsForValue().set(k,v)方法设置一个值opsForValue().get(k)方法获取值
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Test
public void testsetAndGetString() {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name", "happyjava");
String name = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
|
执行结果:
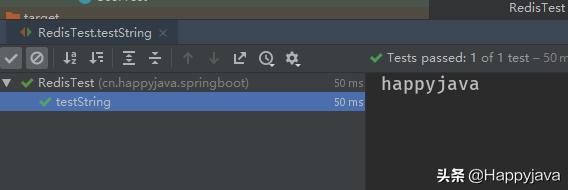
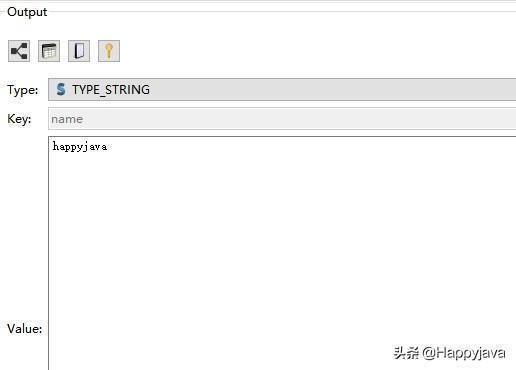
查看redis数据库上的值,如下:
设置值并且同时设置过期时间
opsForValue().set方法还支持同时设置键对应的过期时间
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Test
public void testSetWithExpireTime() {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name2", "happyjava2", 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
String name2 = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name2");
System.out.println(name2);
}
|
执行结果:
获取键的过期时间
我们可以通过redisTemplate.getExpire方法获得键的过期时间
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Test
public void testSetWithExpireTime() {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name2", "happyjava2", 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
String name2 = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name2");
System.out.println(name2);
Long expire = redisTemplate.getExpire("name2", TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println(expire);
}
|
执行结果如下:
设置键的过期时间
我们可以通过redisTemplate.expire方法设置键的过期时间
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Test
public void testSetExpire() {
redisTemplate.expire("name",120,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
Long expire = redisTemplate.getExpire("name", TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println(expire);
}
|
之前设置了name是非过期的,这里给它设置个过期时间。执行结果如下:
getAndSet
我们可以通过opsForValue().getAndSet方法获取此时的值,然后设置一个新的值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Test
public void test() {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name", "123456");
String name = redisTemplate.opsForValue().getAndSet("name", "happyjava3");
System.out.println(name);
name = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
|
输出结果如下:
append追加
通过redisTemplate.opsForValue().append方法可以追加内容。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Test
public void test() {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().append("name","append");
String name = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
|
这里向之前的name键追加了一个字符串“append”,输出结果如下:
自增
自增是redis里非常常用的方法,常常用该方法来实现计数器。我们可以通过redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment方法实现自增
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Test
public void test() {
Long count = redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment("count");
System.out.println(count);
Long count1 = redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment("count", 11);
System.out.println(count1);
}
|
如果键不存在,则会默认从0开始自增,我们也可以设置自增的值的大小。
自减
我们可以通过redisTemplate.opsForValue().decrement方法来实现自减
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Test
public void test() {
Long count = redisTemplate.opsForValue().decrement("count");
System.out.println(count);
Long count1 = redisTemplate.opsForValue().decrement("count", 10);
System.out.println(count1);
}
|
如果存在则设置/如果不存在则设置
setIfAbsent:如果不存在,则设置。

并且可以通过重载的方法设置过期时间,这个方法是很重要的,可以基于该方法实现一个分布式锁。
setIfPresent:如果存在,则设置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Test
public void test() {
Boolean aBoolean = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent("name", "happy");
System.out.println(aBoolean);
Boolean aBoolean1 = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfPresent("name", "happy2");
System.out.println(aBoolean1);
}
|
因为之前已经存在name的值,该代码的预期输出结果是false true。

总结
这里介绍了redis string数据结构的常用操作。接下来的会对其它的数据结构做进一步讲解。

